Other Tests for Celiac Disease
Find out if you are at risk - get tested
| TEST | TESTING TIME | PRICE |
|---|---|---|
| DNA Celiac Disease Test | 4 to 6 weeks | $249 USD |
Bloodwork, Endoscopy & Biopsy of the Small Intestines
Blood tests can be used to detect antibodies that are suggestive of Celiac Disease. These tests may include:
- tissue transglutaminase (TTG) IgA
- endomysial antibody (EMA) IgA
- anti-deamidated gliadin-related peptide (a-DGP) antibodies IgA and IgG
- antigliandin antibody (AGA) IgA and IgG
Individuals with Celiac Disease may also be IgA deficient, therefore these individuals may not have elevated levels of IgA antibodies associated with the disease. In these cases, IgA deficiency may be indicative of Celiac Disease, and testing of TTG IgG antibodies is recommended.
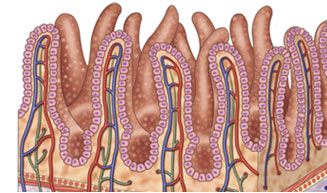
If these blood tests are positive, they are often followed up with endoscopy to biopsy the first section of the small intestine (duodenum). A flattening of the villi along the walls of the intestine is indicative of Celiac Disease.
Dermatitis Herpetiformis Also an Indicator
Dermatitis herpetiformis is an itchy, blistering skin rash that occurs in 15-25% of people with Celiac Disease. Dermatitis herpetiformis can be diagnosed with a blood test and skin biopsy; detection of antibodies associated with Celiac Disease and a positive result of dermatitis herpetiformis indicate that a patient does not require an intestinal biopsy for Celiac Disease. As with Celiac Disease, the rash will respond to a gluten-free diet, but may also require antibiotics for control.
Laboratory Tests
Some other abnormalities in laboratory test results may be suggestive of Celiac Disease. These include:
- low albumin
- high alkaline phosphatase indicating bone loss
- clotting factor abnormalities
- low cholesterol
- indications of anemia by complete blood count
- altered liver enzymes (transaminases)
- prothrombin time


